 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-2320-312-24-2
Systems Operation Section
Aftercooler core (2) is a separate cooler core.
i01538883
Aftercooler core (2) is installed in front of the core
Air Inlet and Exhaust System
(standard) of the engine radiator on the machine.
Air that is ambient temperature is moved across
SMCS Code: 1050
the aftercooler core by the engine fan. This cools
the turbocharged inlet air.
From aftercooler core (2), the air is forced into the
cylinder head in order to fill the inlet ports. Air flow
from the inlet port into the cylinder is controlled by
the inlet valves.
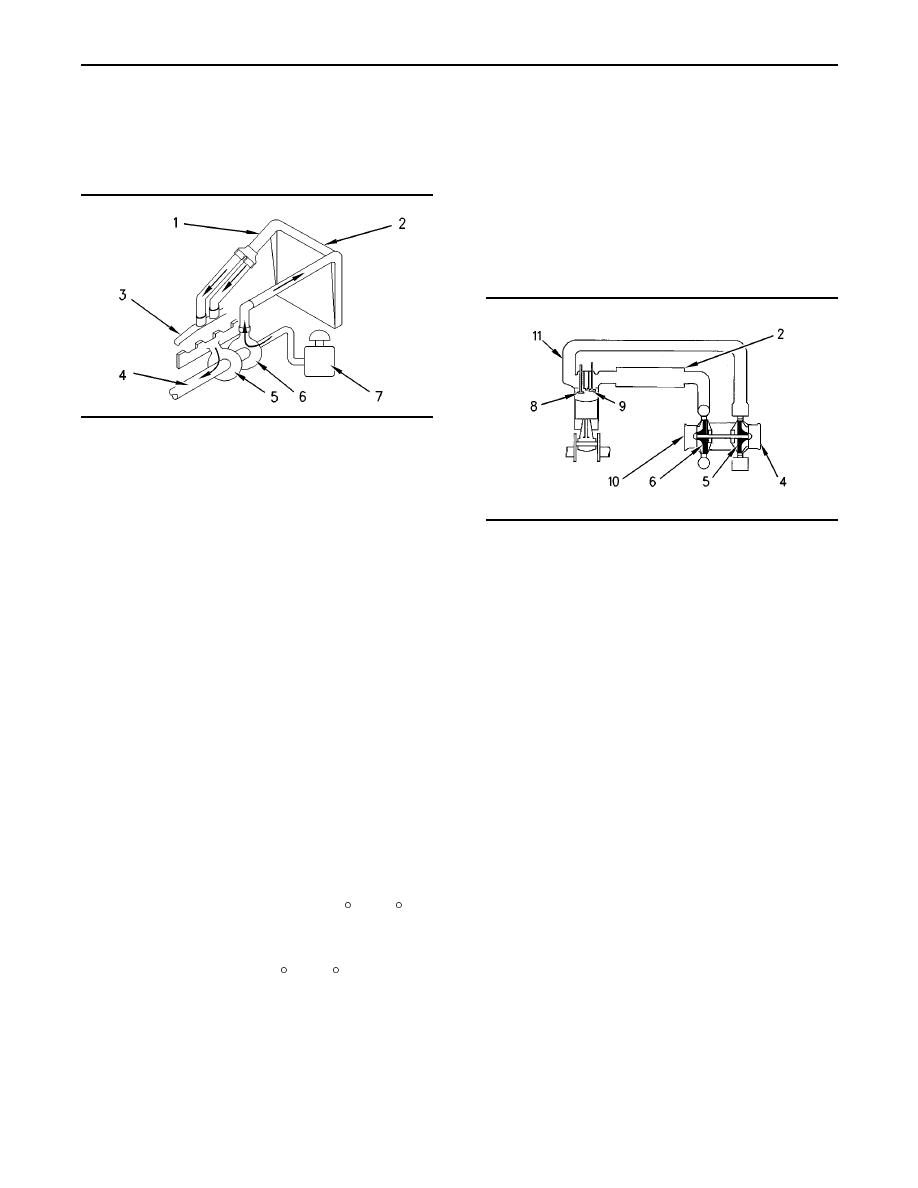
g00787037
Illustration 23
Airflow Schematic
(1) Air line. (2) Aftercooler core. (3) Air inlet elbow. (4) Exhaust
outlet from turbocharger. (5) Turbine side of turbocharger. (6)
Compressor side of turbocharger. (7) Air cleaner.
The components of the air inlet and exhaust system
g00805952
Illustration 24
control the quality of the air that is available for
Air Inlet And Exhaust System
combustion. These components also control the
(2) Aftercooler core. (4) Exhaust outlet. (5) Turbine side of
amount of the air that is available for combustion.
turbocharger. (6) Compressor side of turbocharger. (8) Exhaust
The components of the air inlet and exhaust system
valve. (9) Inlet valve. (10) Air inlet. (11) Exhaust manifold.
are listed below:
There are two inlet valves and one exhaust valve
Air cleaner
for each cylinder. Inlet valves open when the
piston moves down on the inlet stroke. When the
Turbocharger
inlet valves open, cooled compressed air from
the inlet port is pulled into the cylinder. The inlet
Aftercooler
valves close and the piston begins to move up on
the compression stroke. The air in the cylinder is
Cylinder head
compressed. When the piston is near the top of the
compression stroke, fuel is injected into the cylinder.
Valves and valve system components
The fuel mixes with the air and combustion starts.
During the power stroke, the combustion force
Piston and cylinder
pushes the piston downward. After the power stroke
is complete, the piston moves upward. This upward
Exhaust manifold
movement is the exhaust stroke. During the exhaust
stroke, the exhaust valve opens, and the exhaust
Inlet air is pulled through the air cleaner. The inlet air
gases are pushed through the exhaust port into the
is then compressed and heated by the compressor
exhaust manifold. After the piston completes the
wheel of turbocharger (6) to about 150 C (300 F).
exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve closes and the
The inlet air is then pushed through air-to-air
cycle starts again. The complete cycle consists of
aftercooler core (2) and the inlet air is moved to air
four stages:
inlet elbow (3). The temperature of the inlet air at
air inlet elbow (3) is about 43 C (110 F). Cooling
Inlet stroke
of the inlet air increases the combustion efficiency.
Increased combustion efficiency helps to lower fuel
Compression stroke
consumption. Also, increased combustion efficiency
helps to increase horsepower output.
Power stroke
Exhaust stroke
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |