 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
FUEL SYSTEM THEORY OF OPERATION |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 5-2410-237-23
FUEL SYSTEM THEORY OF OPERATION
FUEL FLOW
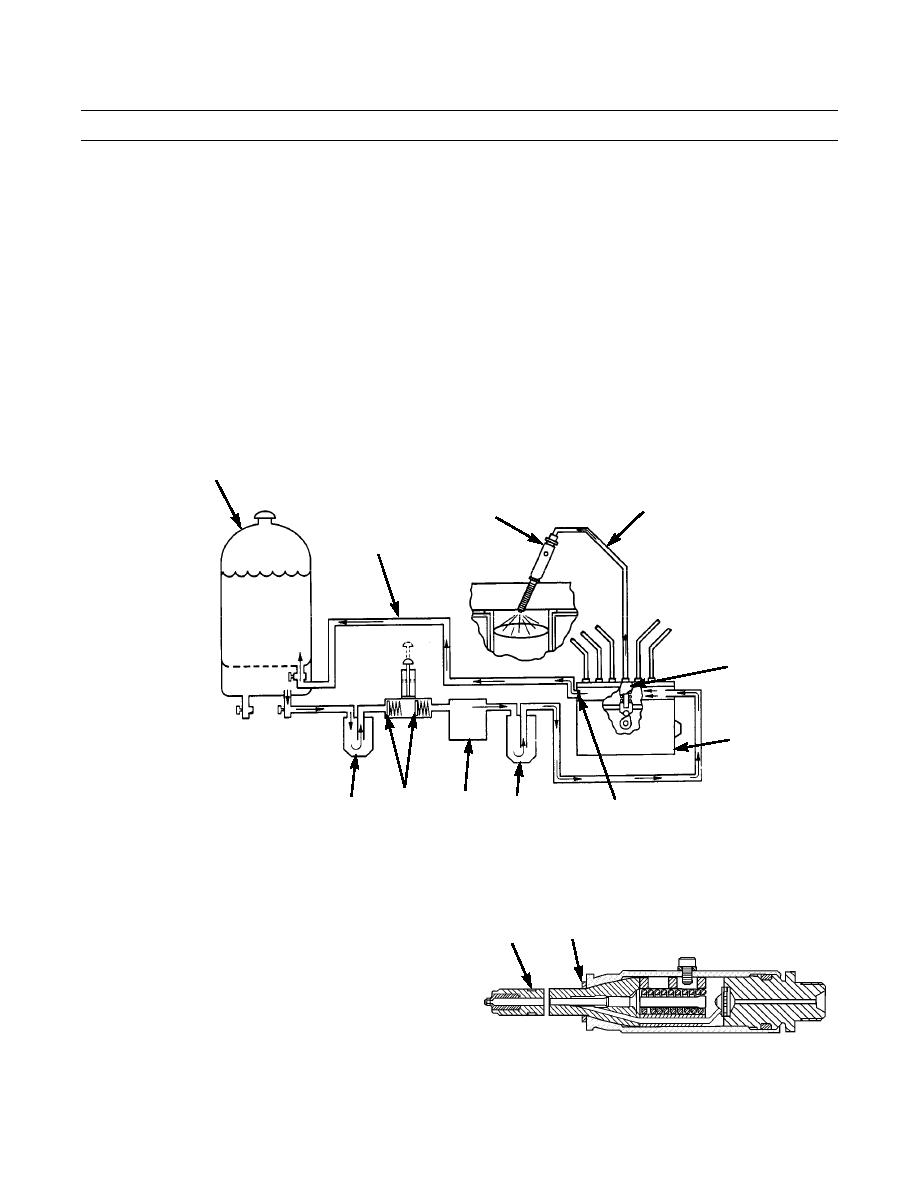
1.
Fuel is pulled from fuel tank (1) through primary fuel filter (2) and priming pump check valves (3) by fuel transfer pump
(4). From the fuel transfer pump, the fuel is pushed through secondary fuel filter (5) and to the fuel manifold in fuel
injection pump housing (6). The pumping spring in the fuel transfer pump keeps the fuel pressure in the system at 25-42
psi (172-290 kPa). Constant bleed orifice (7) lets a constant flow of fuel go though fuel return line (8) back to fuel tank
(1). This helps keep the fuel cool and free of air.
2.
Fuel injection pump (9) gets fuel from the fuel manifold and pushes fuel at very high pressure through fuel line (10) to
fuel injection nozzle (11). The fuel injection nozzle has very small holes in the tip that change the flow of fuel to a very
fine spray that gives good fuel combustion in the cylinder.
FUEL INJECTION PLUNGER AND BARREL
The fuel injection plunger and barrel (9) increases the pressure of the fuel and sends an exact amount of fuel to the fuel
injection nozzle (11). There is one fuel injection plunger and barrel for each cylinder in the engine.
1
10
11
8
9
6
387-171
3
4
5
2
7
FUEL FLOW
FUEL INJECTION NOZZLE
1.
The fuel injection nozzle goes through the cylinder
head into the combustion chamber. The fuel injection
12
13
pump sends fuel with high pressure to the fuel injec-
tion nozzle where the fuel is made into a fine spray for
good combustion.
2.
Seal (12) goes against the cylinder head and prevents
leakage of compression from the cylinder. Carbon
387-172
dam (13) keeps carbon out of the bore in the cylinder
head for the nozzle.
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |