 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Page Title:
Figure 6-42. Oil Pan Gaskets and Seal. |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
|
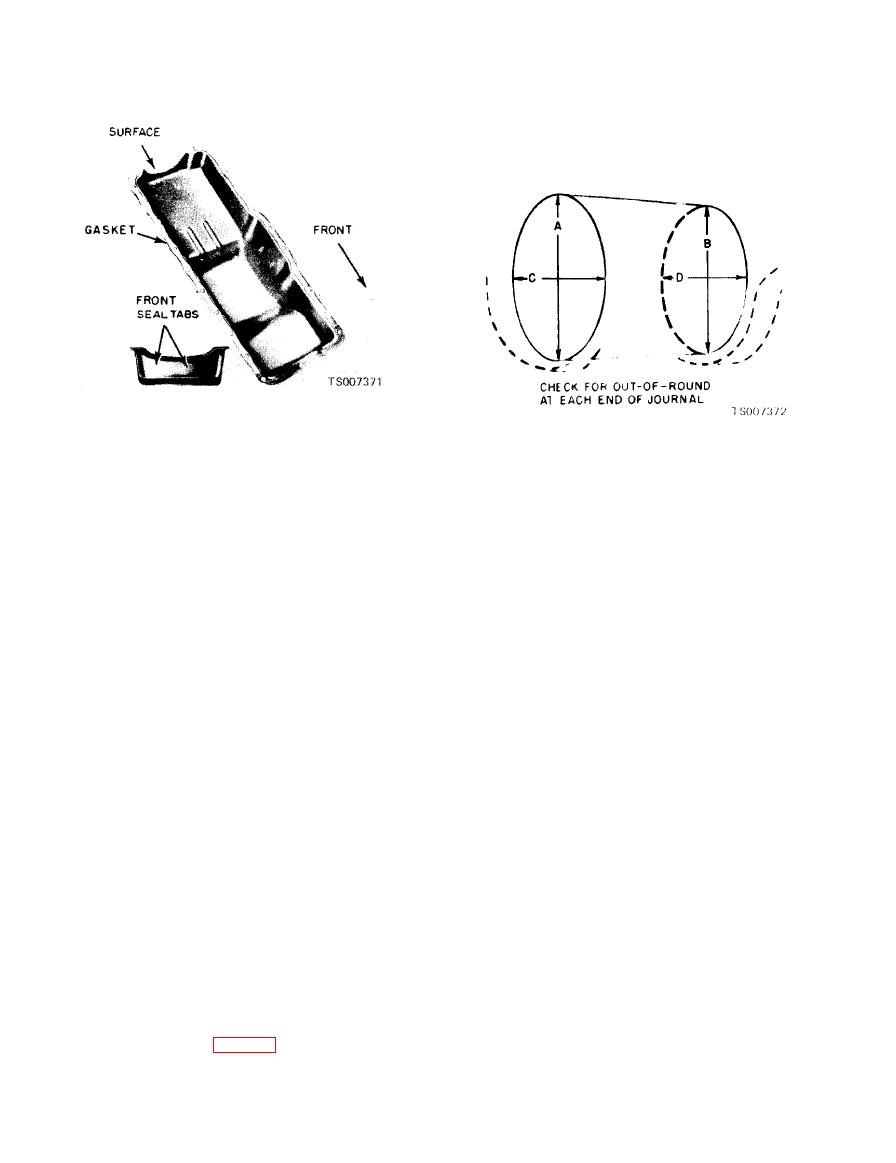 TM 10-3930-633-34
A VS. B = VERTICAL TAPER
C VS. D = HORIZONTAL TAPER
A VS. C AND B VS. D = OUT OF ROUND
a. Cleaning.
(3) Inspect the rear oil seal surface of the
(1) Clean the crankshaft by rinsing in a bath
crankshaft for excessively deep grooves, nicks,
of solvent, Federal Specification P-D-680. Blow
burrs, porosity, or scratches which could damage
out all oil passages with compressed air.
the oil seal lip during installation. Remove all
NOTE
nicks and burrs and polish the chamfered edge
Handle the crankshaft very carefully to avoid
and oil seal contact surface wit h crocus cloth.
possible fractures or damage to the finished bearing
(4) Inspect the crankshaft damper or sleeve
surfaces.
oil seal surface for nicks, sharp edges or burrs
(2) Clean the oil seal surface at the rear of the
that might damage the oil seal during installation
crankshaft with solvent to remove any corrosion,
or cause premature seal wear.
sludge or varnish deposits. Excessive deposits
not readily removed with solvent may be removed
with crocus cloth.
(3) Use crocus cloth to remove any sharp
and cap. Identify the bearings if they are to be
edges, burrs or other imperfections which might
used again. Clean the connecting rod in solvent,
damage the oil seal during installation or cause
including the rod bore and the back of the inserts.
premature seal wear.
Do not use a caustic cleaning solution. Blow out
CAUTION
all passages with compressed air.
Do not use crocus cloth to the extent that
b. Inspection.
the seal surfaces become polished. A
(1) The connecting rods and related parts
finely polished surface may produce poor
should be carefully inspected and checked for
sealing or cause premature seal wear.
conformance to specifications. Various forms of
(4) Clean the oil seal contact surface on the
engine wear caused by these parts can be readily
crankshaft damper or sleeve with solvent to
identified.
remove any corrosion, sludge or varnish deposits.
(2) A shiny surface on the pin boss side of
Excess deposits that are not readily removed with
the piston usually indicates that a connecting rod
solvent may be removed with crocus cloth.
is bent or the piston pin hole is not in proper
b. Inspection.
relation to the piston skirt and ring grooves.
(1) Inspect the main and connecting rod
(3) Abnormal connecting rod bearing wear
journals for cracks, scratches, grooves or scores.
can be caused by either a bent connecting rod, an
(2) Measure the diameter of each journal at
improperly machined journal, or a tapered
least four places to determine out-of-round, taper
connecting rod bore.
or undersize condition (fig. 6-43). Refer to table 6-
(4) Twisted connecting rods will not create
6 for specifications.
an easily identifiable wear pattern, but badly
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |