 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 TM 9-2320-364-34-1
1-12. ELECTRICAL SYSTEM (CONT).
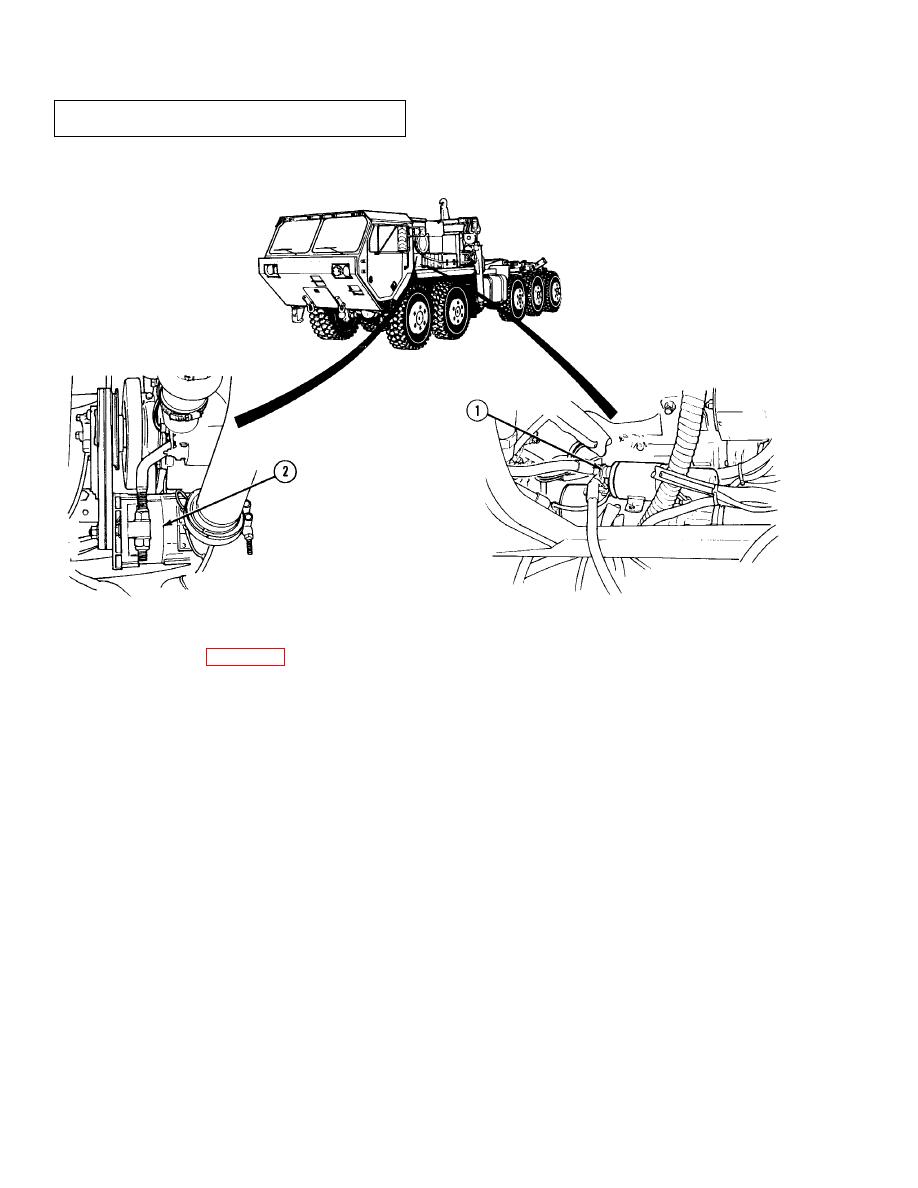
In the electrical system (Figure 1-11) a heavy duty starting motor (1) is mounted on the engine flywheel housing and
provides the cranking power necessary for starting the engine. The DUVAC maintains both a 14- and 28-volt level for
proper battery charging. The alternator (2) provides sufficient amperage to operate all electrical components and
charge the batteries during engine idling. Truck exterior lights are mounted in protective locations or are protected to
prevent damage. Protection is provided for lights during cross country travel. Polycarbonate lenses are provided for
all lights except the sealed beam headlights and service lights. The PLS electrical system supplies all of the electrical
power needed to operate the truck and trailer. The complete electrical system is made up of the following sub-systems:
Power Storage and Generating
Accessory Lighting
Engine Starting and Stopping
Instruments
Service Lighting
Warning Lights and Buzzers
Blackout Lighting
a. Power Storage and Generating. Power storage for the truck consists of four 12-volt batteries. The four
batteries are divided into two sets. Two batteries in each set are wired in parallel to produce higher amperage. The two
sets are then wired in series to produce 24 volts. While the batteries can power all of the systems for a limited time,
their primary purpose is to supply power to the engine's starting system. Once the engine is running, the generating
system provides the electrical power for all of the systems. The engine driven alternator generates alternating current
(AC) which is passed through a set of rectifiers that change it into direct current (DC). This direct current is used to
charge the batteries and is distributed to the other systems of the PLS. The DUVAC adjusts alternator output to fit
the needs of the electrical system.
1-14
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |